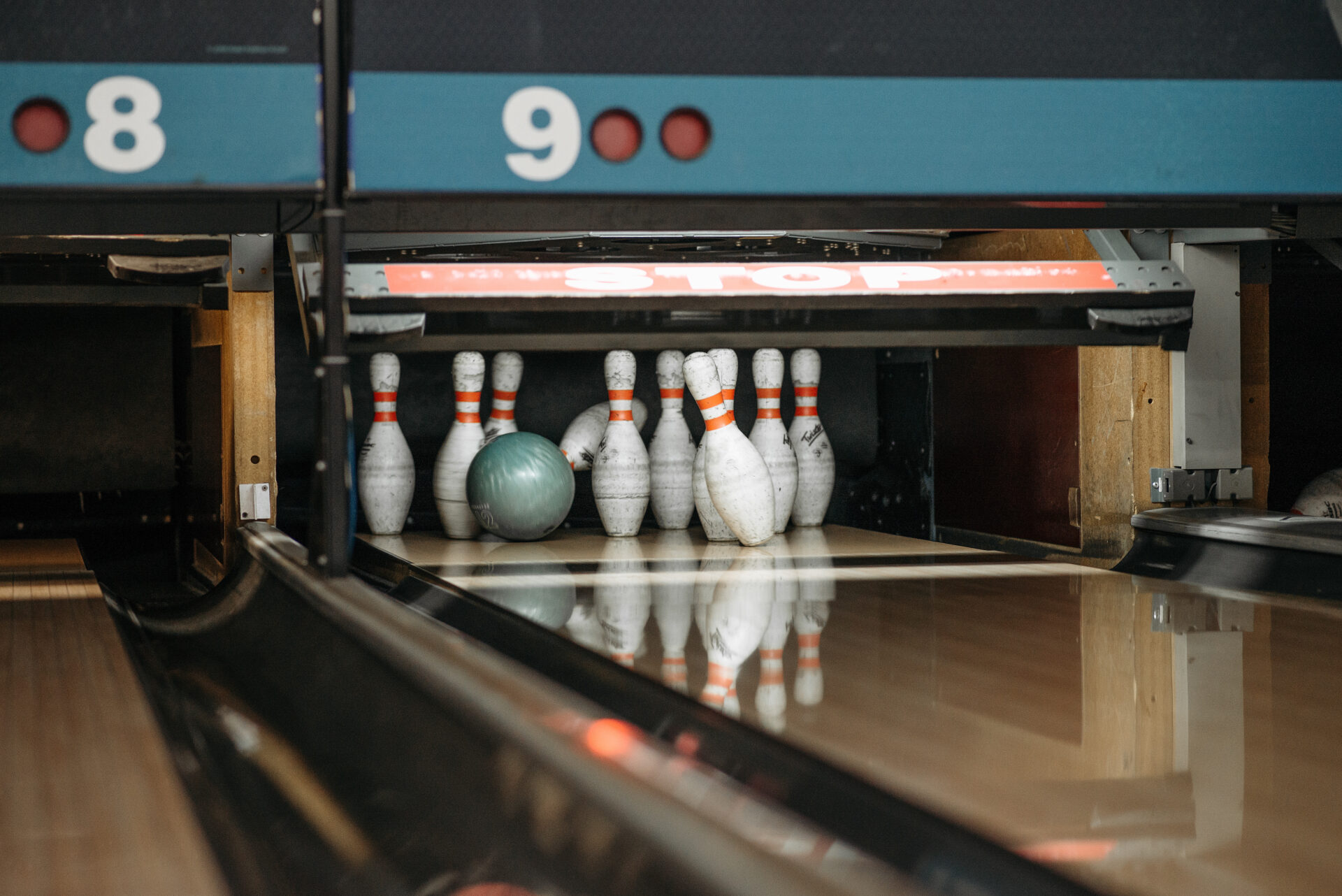
Bowling balls are made of various materials, depending on the type of bowling ball and its intended use. The most common material used to make bowling balls is polyester, which is a type of plastic. Other materials used include urethane, reactive resin, and particle resin. In addition to the material used for the outer shell, bowling balls also contain core materials designed to balance the weight and provide additional control over the ball’s trajectory.A bowling ball is typically composed of a hard outer shell made of plastic, urethane, or reactive resin. Inside the shell is a core, which is often made from a material such as cork or polyester and filled with particles such as tiny glass beads. The core determines the ball’s weight and can change the ball’s trajectory when thrown. Finally, the outer portion of the bowling ball is covered in a thin layer of textured material called a coverstock, which helps to make the ball grip the lane for better control.
What Materials Are Used to Make Bowling Balls?
Bowling balls are typically made of a variety of materials, including urethane, polyester, and plastic. Urethane bowling balls are the most popular type since they provide a combination of control and power. Urethane bowling balls have a special coverstock that helps them grip the lane better and provide more hook potential. Polyester and plastic bowling balls are less expensive than urethane models and offer less hook potential. Plastic bowling balls are ideal for beginners as they are easier to control. They also come in various colors and patterns, making them attractive to bowlers of all skill levels.
No matter what material is used to make a bowling ball, it must meet certain specifications set by the USBC (United States Bowling Congress). This includes weight, circumference, hardness rating, and size. The weight of a typical adult-size ball ranges from 6-16 lbs (2.7-7.3 kg), with 12 lbs (5.4 kg) being the most common weight for adults. The circumference should be 26-27 inches (66-68 cm) for an adult male or 24-25 inches (61-63 cm) for an adult female. The hardness rating should be between 70 and 90 on the Shore Durometer scale.
What is the Core of a Bowling Ball Made Of?
The core of a bowling ball is the heaviest part and is typically made up of a hard material such as urethane, polyester, or even resin. This material allows the ball to stay in motion while also providing stability and control to the player. The core’s shape and size are important factors in determining how the ball will react when it hits the pins. The core can be round, oval, or even asymmetrical depending on the type of bowling ball. Additionally, cores are usually filled with sand or gel to add weight and balance to the ball.
The coverstock of a bowling ball refers to the outer layer that covers and protects the core. It is usually made from polyester or urethane and is designed to provide traction between the lane and the bowler’s hand. Coverstocks come in various colors, textures, and patterns that can affect how a ball performs when thrown down the lane. Additionally, coverstocks help reduce friction between the lane surface and the bowling ball.
The weight block typically sits directly beneath the coverstock and provides additional weight for increased momentum when throwing a bowling ball. Weight blocks are usually composed of lead or tungsten alloy material that helps give more power to your throw. The shape of these blocks can also vary depending on what type of bowling you are playing as well as your style of throwing.
Finally, bowling balls have an interior shell which helps keep all components together. This shell is typically made from plastic or rubber-based materials which help protect all interior components from damage over time. Additionally, shells also aid in producing consistent spins when thrown down a lane for better control over your shots.
Overall, bowling balls are complex pieces of equipment that require several different components in order for them to function properly. Understanding each component can help you choose better equipment based on your skill level and preference so you can maximize your performance at every game!
What Is the Coverstock of a Bowling Ball Made Of?
The coverstock of a bowling ball is made of a variety of materials, such as urethane, reactive resin, and plastic. The type of coverstock that is used depends on the desired performance characteristics and the price range. Urethane is generally considered to be the most durable and highest performing type of coverstock, as it provides excellent hook potential and can withstand repeated strikes with minimal damage. Reactive resin coverstocks are typically slightly cheaper than urethane, but they also provide good hook potential and durability. Plastic coverstocks are usually the least expensive option, but they do not provide as much hook potential or durability as their more expensive counterparts.
The Manufacturing Process for Bowling Balls Differ Between Brands
The manufacturing process for bowling balls differs between brands, and it is important to know what to look for when choosing the right ball. The core material, coverstock, finish, drilling technique, and hook potential are all factors that affect the performance of a bowling ball.
The core material is the innermost foundation of the ball and is the most crucial part of the manufacturing process. It affects the dynamic balance and weight block shape which determines how the ball will react on the lane. Different brands use different materials such as polyester, urethane, or reactive resin to create their bowling balls.
Coverstock is a term used to describe the outer shell of a bowling ball and can affect lane grip, hook potential, and overall reaction on a lane. Different types of coverstock are designed to perform differently on different types of lanes. Urethane coverstocks are best suited for dry lanes while reactive resin coverstocks are best suited for oily lanes.
The finish also affects how a bowling ball will react on a lane. The most common finishes used in bowling balls are shiny polished and dull sanded. Shiny polished finishes produce less friction with the lane surface than dull sanded finishes which cause more friction with the lane surface allowing it to hook more aggressively.
Drilling techniques can also affect how a bowling ball reacts on a lane. Different drilling techniques can alter where weight blocks are placed in relation to fingers holes which can cause different reactions on different types of lanes and surfaces.
Finally, hook potential affects how much spin is put on a bowling ball when it is thrown down a lane which influences its reaction on dry or oily surfaces. Higher hook potential causes more spin which allows bowlers to control their shots better when playing on oily lanes while lower hook potential allows bowlers to throw straighter shots when playing on dry lanes.
To summarize, understanding what goes into making each brand of bowling balls is essential in order to choose one that best suits your game style and performance needs. From core material to finish, drilling technique and hook potential – each factor plays an important role in determining how well your chosen ball will perform once it hits those pins!
How Are Different Types of Bowling Balls Made?
Bowling balls are made using a variety of materials and production methods. The two main types of bowling balls are plastic and urethane. Plastic bowling balls are the most commonly used, while urethane bowling balls offer more spin and control.
Plastic bowling balls are usually made by injection molding, where the molten plastic is poured into a pre-formed mold. The plastic is then cooled and hardened to form the ball shape. After this, the surface of the ball is sanded down to remove any imperfections and polish the finish. The coverstock, which is the outer layer of material on a bowling ball, is then added on top to give it an attractive look and feel as well as provide traction when it comes in contact with the lane surface.
Urethane bowling balls are made using a similar process but with different materials. Instead of molten plastic, urethane is used to form the core of the ball. Urethane is also used to make up the coverstock, although some manufacturers may use a hybrid of urethane and plastic for added durability and performance benefits. Urethane offers more grip than plastic when it comes in contact with the lane surface, making it ideal for advanced bowlers who need more control over their shots.
After both types of bowling balls have been formed and covered with material, they must be tested for performance characteristics before they can be sold to consumers. This testing involves rolling them down a simulated lane surface to measure speed, hook potential, break point reactions, and other factors that affect playability on real lanes. Only after passing this test do they get approved for sale by manufacturers.
Reactive Resin
Reactive resin is a type of ball construction that is used in a wide variety of sports, including bowling, tennis, and golf. This type of ball construction involves the use of a two-part resin system that allows for the bonding of multiple components together. The two parts are a hardener and a base resin which are mixed together to create an extremely strong bond between the components. Reactive resin balls are known for their strength and durability, making them an ideal choice for athletes who need to rely on their equipment to perform at its best.
Urethane
Urethane is another type of ball construction that is commonly used in sports such as tennis and golf. This type of construction involves the use of a urethane material that is applied around the core of the ball, creating a more durable layer than standard rubber or plastic materials. Urethane balls are known for their superior bounce characteristics as well as their enhanced control capabilities when compared to other types of ball constructions. Additionally, urethane balls can also provide improved levels of accuracy due to their reduced spin rate when struck by an object.
Particle Balls
Particle balls are a relatively new type of ball construction that has been gaining popularity in recent years. This type of construction involves using small particles such as cork or rubber which are held together by heat-sensitive adhesive compounds. Particle balls offer increased levels of durability and control due to their unique construction, making them an ideal choice for athletes who need reliable equipment which can withstand constant use without deteriorating over time.
How Does the Weight Block Affect a Bowling Ball’s Performance?
The weight block of a bowling ball is an important factor in determining its performance. The weight block is a heavy piece of material located near the center of the ball and it affects the ball’s balance and momentum. It helps to increase the speed of the ball and also helps to create hook and spin on shots.
The size and shape of the weight block, as well as its location, can have a significant effect on how a bowling ball performs. If the weight block is too small or too light, it can reduce the speed of the shot and make it difficult to control. On the other hand, if it is too large or too heavy, it can cause excessive hooking and spinning which can be difficult to manage.
In general, heavier balls tend to travel further with more spin on them than lighter balls, while lighter balls tend to be more controllable with less spin. It is important to select a weight block that matches your style of play so that you can achieve optimal performance out of your bowling ball.
The type of material used for the weight block also plays an important role in how well it affects a bowling ball’s performance. Blocks made from harder materials such as brass will produce more hooking action than blocks made from softer materials such as lead or plastic.
Overall, understanding how weight blocks affect a bowling ball’s performance can help you find just the right balance between speed and control for your style of play. Experimenting with different types and sizes of weight blocks will help you determine which one works best for you so that you can maximize your performance when playing bowling.

Conclusion
Bowling balls are made up of a variety of materials, including polyester, urethane, reactive resin, and particle. Each material has its own unique properties that make it suitable for different bowlers and conditions. Polyester balls are the most affordable and durable, while resin and urethane balls provide more hook potential. Particle-filled balls offer a combination of control and hook potential.
The most important factor in choosing a bowling ball is finding the one that best suits your style of play. The weight and coverstock should be matched to your skill level and bowling environment. A ball with the right characteristics can help you improve your game by reducing skid length, increasing back-end reaction, and improving accuracy.
No matter what type of bowling ball you choose, it is important to take care of it properly in order to keep it in top condition for years to come. Regular maintenance such as cleaning and polishing will help preserve the performance characteristics of the ball. With proper care, your bowling ball will serve you well for many years!




